Can you walk with a fractured tibia? If you’ve just injured your shinbone or are worried about someone who has, this question is probably on your mind.
A fractured tibia can cause sharp pain, swelling, and make standing or walking feel impossible. But what does that really mean for your mobility? Can you put any weight on your leg? Should you try walking, or is it better to rest completely?
Understanding what your body needs right after a tibia fracture is crucial—not only to ease your pain but also to heal properly and avoid further damage. You’ll discover when walking is safe, what signs to watch for, and how to support your recovery step by step. Keep reading to learn how to protect your leg and get back on your feet the right way.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Tibia Fracture Symptoms
- 2 Immediate Actions After Injury
- 3 Walking With A Fractured Tibia
- 4 Risks Of Walking Too Soon
- 5 Treatment Options
- 6 Recovery Timeline
- 7 Tips For Safe Mobility
- 8 Preventing Future Injuries
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Tibia Fracture Symptoms
A fractured tibia causes clear and painful symptoms. Recognizing these signs helps in seeking quick treatment. The tibia, or shinbone, is crucial for walking and weight support. A break in this bone demands immediate care to avoid complications.
The symptoms often start right after the injury. They can vary in severity but usually include intense pain and swelling. Some signs may be visible, while others affect movement and sensation. Understanding these symptoms is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Severe Pain And Swelling
Intense pain occurs immediately at the injury site. The pain usually worsens with any movement or pressure. Swelling appears quickly, making the leg look puffy and tender. This swelling can limit joint movement and increase discomfort.
Inability To Bear Weight
Standing or walking becomes very difficult or impossible. The broken tibia cannot support the body’s weight. Trying to walk may cause sharp pain or instability. Many people need crutches or a wheelchair for mobility.
Visible Deformity And Bruising
The leg may look crooked, bent, or shorter than normal. Bruises often appear around the fracture area due to blood leaking under the skin. The skin may show dark purple or blue marks. These signs are strong indicators of a serious break.
Numbness And Limited Motion
Numbness or tingling can occur below the fracture. This sensation means nerves may be affected by the injury. Movement in the knee or ankle might be limited or painful. Stiffness develops if the leg stays immobile too long.
Signs Of Open Fracture
Bone may stick out through the skin, creating an open wound. This is a medical emergency due to infection risk. The area bleeds heavily and causes severe pain. Immediate hospital care is necessary to clean and stabilize the injury.
Immediate Actions After Injury
Knowing what to do right after a tibia fracture is vital. Immediate actions can prevent more harm and ease pain. Quick care sets the stage for proper healing and recovery. This section explains the key steps to take after injury.
When To Seek Emergency Care
Seek emergency care if the leg shows severe deformity or bone sticks out. Intense pain that does not ease with rest is a red flag. Loss of feeling or movement in the foot needs urgent attention. Heavy bleeding or open wounds around the injury require fast medical help. Do not delay if you see any of these signs.
Initial First Aid Steps
Keep the injured leg still and avoid moving it. Apply a clean cloth to stop any bleeding. Use ice wrapped in a towel to reduce swelling and pain. Elevate the leg above heart level if possible. Avoid putting weight on the leg. Call for medical help or get to a hospital as soon as possible.
Avoiding Further Damage
Do not try to straighten the leg or push bone back in. Avoid walking or standing on the injured leg. Do not remove any objects stuck in wounds; let professionals handle them. Use splints or padding to support the leg during transport if trained. Handle the injured person gently to prevent more injury.
Walking With A Fractured Tibia
Walking with a fractured tibia requires careful management and patience. The tibia, or shinbone, is a major bone that supports most of the body’s weight during walking. After a fracture, putting weight on the leg too soon can delay healing or cause further injury. Understanding the rules for walking and support helps ensure a smooth recovery. Medical advice usually guides the process based on the fracture’s severity and type.
Weight-bearing Restrictions
Most patients cannot put weight on a fractured tibia right away. Doctors often recommend non-weight bearing at first. This means keeping the injured leg off the ground completely. Partial weight bearing might start weeks later. The timeline depends on X-rays and healing progress. Following these restrictions prevents the bone from shifting or breaking again.
Use Of Crutches And Walkers
Crutches and walkers help keep weight off the broken leg. They provide balance and support while moving. Crutches require arm strength and practice to use correctly. Walkers offer more stability but can be bulky. Choosing the right device depends on personal comfort and doctor advice. Using these tools properly reduces pain and risk of falling.
Knee Braces And Support Devices
Knee braces protect the tibia and control movement. They help stabilize the leg and prevent sudden twists. Braces also reduce swelling by providing gentle compression. Some patients use inflatable or rigid braces based on injury type. Support devices improve confidence during walking and protect healing tissues.
Progression From Non-weight Bearing To Full Weight Bearing
Healing usually begins with no weight on the leg. Next comes partial weight bearing, adding small amounts of pressure. Physical therapy often guides this step-by-step process. Muscle strength and joint motion improve with controlled activity. Full weight bearing returns only after the bone is strong enough. Rushing this stage can cause setbacks or new fractures.
Risks Of Walking Too Soon
Walking too soon on a fractured tibia can cause serious problems. The bone needs time to heal properly. Putting weight on it early can slow down recovery and cause more harm. Understanding these risks helps protect your leg and avoid extra pain or injury.
Delayed Healing And Complications
Walking before the bone is ready can delay healing. The fracture might take longer to mend or may not heal fully. This can lead to complications like infections or the need for surgery. Rest and limited movement help the bone knit back together correctly.
Increased Pain And Swelling
Putting pressure on a broken tibia causes more pain. Swelling can increase around the injury site. This extra inflammation makes it harder to move and slows the healing process. Pain signals the body that the bone needs rest.
Potential For Bone Misalignment
Walking too early may shift the broken bone parts out of place. Misalignment causes poor bone healing and deformity. This can lead to long-term issues with walking and leg strength. Proper immobilization keeps the bone aligned for correct recovery.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for a fractured tibia depend on the fracture’s severity and location. Proper care is essential for healing and regaining mobility. Some fractures heal well without surgery. Others require surgical repair to align the bone correctly. Therapy plays a key role in restoring strength and movement. Understanding these options helps manage recovery effectively.
Non-surgical Management
Non-surgical treatment suits stable and simple fractures. Doctors may use casts or braces to keep the bone in place. Crutches or walkers help avoid putting weight on the leg. Pain relief and swelling control are important during healing. Regular X-rays track bone repair. This method avoids surgery risks but needs strict rest and care.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery becomes necessary for complex or unstable fractures. Surgeons use plates, screws, or rods to fix the bone. This ensures proper alignment and faster healing. Surgery also helps if the bone breaks through the skin. Post-surgery, patients may still need to limit weight-bearing. Risks include infection and longer recovery time. Surgeons aim for the best function and pain relief.
Physical Therapy And Rehabilitation
Physical therapy starts after initial healing or surgery. Therapists guide gentle exercises to improve motion and strength. Rehabilitation prevents stiffness and muscle loss. Walking aids are gradually removed as strength returns. Therapy focuses on balance and coordination. Regular sessions speed up return to normal activities. Recovery varies but commitment to therapy is key.

Credit: thekitchenprescription.com
Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline for a fractured tibia varies by injury type and treatment method. Understanding each stage helps set realistic expectations. The healing process is gradual and requires patience. Walking too soon can cause complications. Following medical advice ensures a safer recovery.
Healing Phases
The healing of a fractured tibia happens in stages. First, the body forms a blood clot around the break. This clot turns into soft tissue called callus. Over weeks, the callus hardens into new bone. The bone then remodels to regain strength. Each phase takes time and proper care.
When To Start Walking
Walking depends on fracture type and doctor guidance. Most patients start with no weight on the leg. Crutches or walkers help during this phase. Partial weight-bearing may begin after 6 to 8 weeks. Full weight-bearing starts only when the bone is strong. Early walking risks delaying healing or causing pain.
Expected Full Recovery Duration
Full recovery can take 3 to 6 months or longer. Simple fractures heal faster than complex breaks. Physical therapy helps regain movement and strength. Swelling and pain reduce gradually over time. Regular check-ups confirm proper bone healing. Patience and care improve recovery success.
Tips For Safe Mobility
Maintaining safe mobility with a fractured tibia is vital for healing and comfort. Moving carefully helps prevent further injury and supports recovery. Follow practical tips to keep your leg stable while staying as active as possible. Proper techniques and exercises protect your joints and muscles during this challenging time.
Using Assistive Devices Correctly
Crutches, walkers, or knee braces help reduce weight on your injured leg. Always adjust these devices to fit your height and comfort. Place your weight on your hands and the uninjured leg, not the fractured tibia. Move slowly and avoid rushing to prevent falls or extra pain. Clean the tips of crutches often to avoid slipping on smooth surfaces.
Exercises To Maintain Joint Flexibility
Gentle motion keeps your knee and ankle joints flexible. Try simple range-of-motion exercises daily, such as bending and straightening your knee. Avoid putting weight on the leg unless your doctor says it is safe. Moving your toes and ankle can reduce stiffness and improve blood flow. These exercises speed up recovery and keep your joints healthy.
Preventing Muscle Atrophy
Muscle loss happens quickly without movement. Focus on isometric exercises that tighten muscles without moving the bone. For example, press your thigh muscles firmly while resting your leg. Use your uninjured leg for strength training, which helps maintain overall fitness. A physical therapist can guide you in safe exercises to protect muscles during healing.

Credit: prescottazorthopedics.com
Preventing Future Injuries
Preventing future injuries after a fractured tibia is essential for long-term health. The bone needs time to heal fully. Strengthening your leg helps protect it from new damage. Using the right footwear supports your recovery. Moving safely reduces the risk of falls or strain. These steps build a strong foundation for walking again.
Strengthening Exercises
Start with gentle exercises that improve muscle strength. Focus on the calf, thigh, and shin muscles. Strong muscles absorb shock and support the bone. Simple movements like leg lifts or ankle circles work well. Increase intensity slowly under a doctor’s guidance. Avoid high-impact activities until fully healed.
Proper Footwear And Support
Wear shoes that fit well and cushion your feet. Choose shoes with good arch support and a firm sole. Avoid high heels or worn-out shoes. Use braces or supports if recommended by your doctor. Proper footwear helps keep your leg stable. It lowers the chance of twisting or slipping.
Safe Movement Practices
Take small, careful steps when you start walking again. Use assistive devices like crutches if needed. Avoid uneven surfaces and slippery floors. Keep your posture straight and balanced. Listen to your body and stop if you feel pain. Safe movements help your leg heal without extra stress.
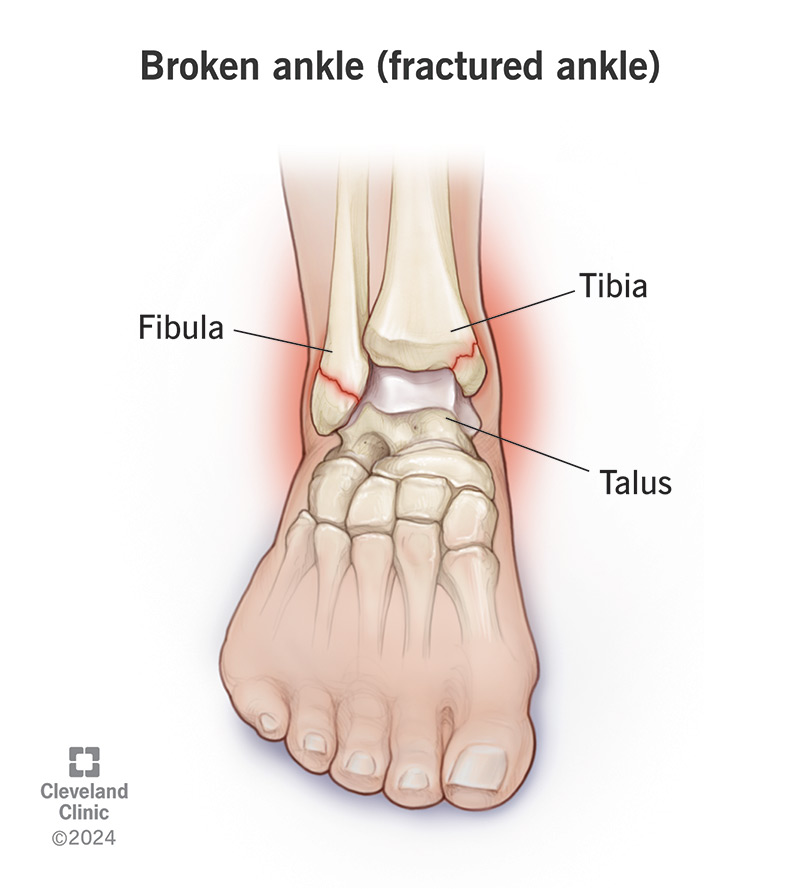
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Walk On A Slightly Fractured Tibia?
Walking on a slightly fractured tibia is generally not advised. Avoid putting weight on the leg to prevent worsening. Use crutches or a brace for support. Follow your doctor’s guidance for healing and mobility exercises.
How Can You Tell If Your Tibia Is Fractured?
A fractured tibia causes severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight. The leg may look deformed or bone may protrude. You might hear a popping sound and feel numbness or limited movement. Seek immediate medical care for diagnosis and treatment.
Can I Bend My Knee With A Fractured Tibia?
Bending your knee with a fractured tibia may cause severe pain and worsen the injury. Follow your doctor’s advice on movement and rehabilitation.
Can A Tibia Fracture Go Unnoticed?
A tibia fracture can sometimes go unnoticed if it’s a minor stress fracture with mild pain. Severe fractures cause immediate, intense pain, swelling, and difficulty walking, making them hard to miss. Always seek medical evaluation for persistent leg pain or swelling.
Can You Walk With A Fractured Tibia?
Walking with a fractured tibia is generally not safe. Most patients must avoid putting weight on the leg to allow healing. Using crutches or a wheelchair is often necessary.
Walking with a fractured tibia is usually not possible right after injury. The leg often feels very painful and weak. Using crutches or a walker helps avoid putting weight on the leg. Following your doctor’s advice speeds up healing and avoids complications.
Gentle movement can prevent stiffness but should be done carefully. Healing times vary, so patience is key during recovery. Always watch for signs of worsening pain or swelling. Proper care ensures the best chance to walk again safely.

